Nucleus Cell Definition
The Cell Nucleus is the substantial and particulate module of the cell. The nucleus is existing in all the cells but matured mammalian erythrocytes cells lack the nucleus. Structure of the nucleus is very complex. The nucleus has about 4-6µm diameter. The nucleus is enclosed by a Peri-nuclear wrapping. There are various numbers of pores present on the nuclear envelope. The outer membrane of the nuclear envelope fuses with the inner membrane to form pores. Nucleus Function is described below:
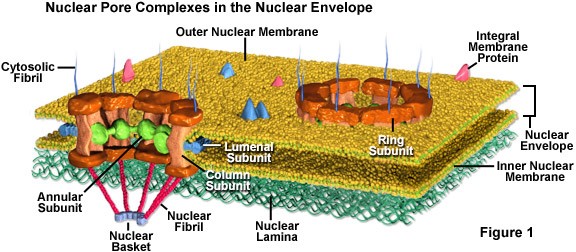
Structure of Nuclear Pores (Structure of Cell Nucleus)

Nuclear pores provide contentiousness among the cytosol and the inner stuffing of the nucleus (nucleoplasm). The electron microscopic studies disclose that nuclear content comprises granular or fibrillar structures.
You May Also Like: Plant Cell Wall – Structure & Function Plant Cell
Structure of Nucleus
Nucleus Structure is described below:
The nucleus is a spherical shape organelle exist in each Eukaryotic cell. Inside the cell nucleus, there is a viscous liquid is presently called Nucleoplasm. It is the analogous viscous liquid to the cytoplasm that found outside the nucleus. The nucleolus, a detached body within the nucleus.
Nucleolus Function
Nucleolus comprises Ribonucleic acids (RNA). The furthermost significant component of the nucleus is a systematized cluster of the thread-like structure called chromatin. Chromatin dispersed throughout all nucleus. chromatin comprises the maximum amount of the cellular deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA). Beforehand of the cell division chromatin arranged into the simple thread-like structures known as chromosomes that will, in the end, be distributed equally to each daughter cell.

Nucleus Function
Nucleus Function
Functions of Nucleus are described below:
- Nucleus takes part in cell division.
- The nucleus contains DNA molecules that are genetic carriers.
- controls the heredity characteristics of an organism.
- It is responsible for protein synthesis, cell division, growth, and differentiation.
- Stores heredity material in the form of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) strands.

- Also stores proteins and ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleolus.
- It is a site for the transcription process in which messenger RNA (m RNA) are produced for protein synthesis.
- Aids in exchange for DNA and RNA (heredity materials) between the nucleus and the rest of the cell.
- Nucleolus produces ribosomes and is known as protein factories.
- It also regulates the integrity of genes and gene expression.
Nucleus Function in Animal Cell

Nucleus Function in Plant Cell


