Introduction of Mitochondria
Introduction of Mitochondria: Mitochondria are characteristically round to oval. Mitochondria are the chief particulate components of the cytoplasm. Mitochondria characterize up to 15% -20% of the dry weight of the cell. Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelle. Mitochondria found in the cytoplasm of almost all eukaryotic cells (cells with clearly defined nuclei).
Size of Mitochondria
The principal function of Mitochondria to generate large quantities of energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondria vary in figure (spherical, filamentous, sausage-shaped) and size (0.5 to 3μ long 0.1 to 0.6μ wide). Mitochondria Location is also described below:
Structure of Mitochondria:
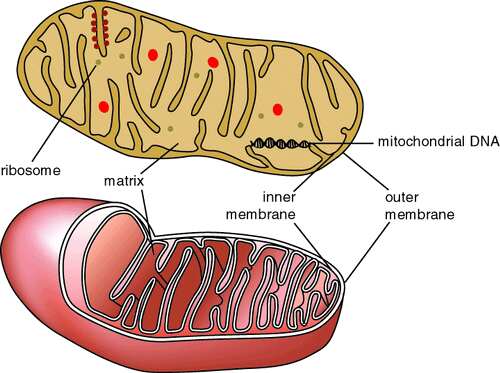
Introduction of Mitochondria: The inner membrane of Mitochondria is very much creased (folded) to form shelf-like structures called Cristae. The width of Cristae vary. These shelf-like structures, known as internal ridges or Cristae. Cristae ranged into the matrix of the mitochondrial structure. In the mitochondrial internal structure, two structurally diverse space are present that can be eminent as, the intra cristae space and the matrix space.
Mitochondria Diagram

Electron microscopic studies show that a mitochondrion has two membranes inner and outer which are separated from each other by 50 to 100oa. The outer and inner layers differ in lipid composition and in enzyme content.
The matrix space of Mitochondria is rich in enzymes. The inner membrane of Mitochondria shows the presence of knob-like structures, which are the site of proteins involved in biological oxidations.
The number of Mitochondria fluctuates with the size and energy necessities of the cell. Flight muscles in birds contain the abundant amount of mitochondria when compared to any other parts of the body.
You May Also: Cell Nucleus | Introduction | Structure | Functions
Functions of Mitochondria:
Mitochondria Facts are described below:
- The mitochondria are the ‘Power Houses’ of the cell.
- In Mitochondria carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids are oxidized to CO2 and H2O by the use of molecular oxygen O2, and the free set energy is stored in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
- In Mitochondria enzymes that involved in this energy, the conversion is in the inner membrane.
- The most important function of mitochondria is to produce energy.
- Mitochondria involved in phosphorylation. The modest molecules of nutrition are sent to the mitochondria to be administered and to yield charged molecules. These charged molecules combine with oxygen and ATP molecules produced. This process is known as oxidative phosphorylation.
- Mitochondria support the cells to maintain the appropriate concentration of calcium ions inside the cubicles of the cell.
- The mitochondria also support building convinced parts of blood and hormones like testosterone and estrogen.
- The liver cells mitochondria have enzymes that detoxify ammonia.
- The mitochondria also play a significant role in the process of apoptosis or programmed cell death.
- Abnormal death of cells owing to the dysfunction of mitochondria can disturb the function of the organ.
Mitochondria Analogy

Mitochondrial Disease Symptoms

