Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis Definition
What is Gluconeogenesis: Gluconeogenesis means that “the production of new glucose”. Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metallic pathway that generates glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrate including glycerol, lactate, and glucogenic amino acid. It occurs around 8 hours of fasting when liver glycogen stores deplete continually and alternative source of glucose is needed. It occurs in the liver and kidney.
There are three main precursors; lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acid. Lactate is from anaerobic glycolysis in the exercise of muscles, and red blood cell is from the Cori Cycle; Glycerol is released from adipose tissue which is the breakdown of triglycerides and amino acid. It is the creation of glucose and has a close relationship with glycolysis.
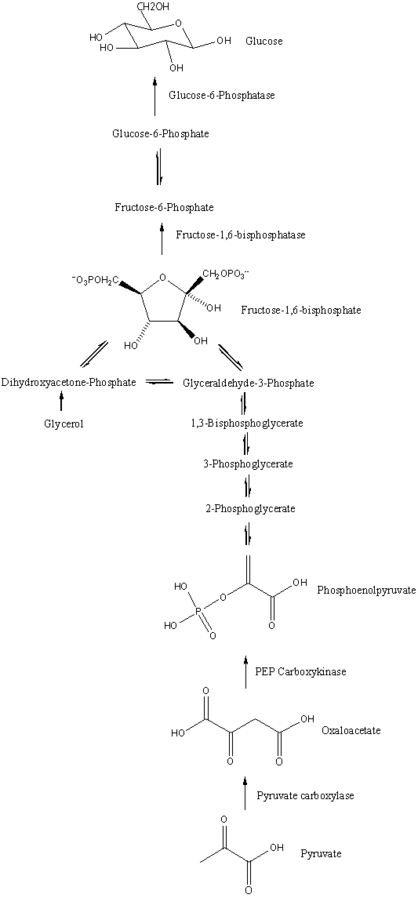
It is the process in which glucose produces when glycolysis breaks. Although, It is complex as reversing of glycolysis occurs and there are irreversible steps in glycolysis. For the circumvent of gluconeogenesis, more enzymes work together as Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) that helps in converting fructose 1, 6-bisphosphatase to fructose 6-phosphate. In the end, glucose-6-phosphate turns to glucose.
Where does Gluconeogenesis occur
Where does Gluconeogenesis occur in the cell: Within Invertebrates, it happens mostly in the liver. And sometime within the cortex of the kidneys but at a very small rate, it will happen. In ruminants or many other animals, it is basically a dependable procedure. In several different creatures, this procedure will happens during the times of fasting, starvation, low-starch diets, or extreme exercise.
When does Gluconeogenesis occur

Gluconeogenesis Pathway:
- It starts in either the cytoplasm or mitochondria of the liver or kidney. Two pyruvate molecules carboxylates to produce oxaloacetate.
- Oxaloacetate reduces malate by NADH so it can be transported out of mitochondria.
- Malate is oxidized back to oxaloacetate after it out form mitochondria.
- Enzyme PEPCK used by phosphoenolpyruvate which formed by oxaloacetate.
- Phosphoenolpyruvate change in fructose-1, 6-phosphate and then to fructose-6-phosphate. ATP also used during this process
- Fructose-6-phosphate becomes a change into glucose-6-phosphate along the enzyme phosphoglucoisomerase.
- Glucose is made by glucose-6-phosphate in the endoplasmic reticulum cell via the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate. A phosphate group is removed in order to form glucose, and glucose-6-phosphate and become glucose and ADP.
The function of Gluconeogenesis:
Our body needs It to produce glucose which helps to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Glucose is used by cells that make the energy molecule of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). When a person has not eaten anything as during the period of famine or starvation, gluconeogenesis occurs at this time.
A person without eating food has become a low sugar level. The body does not have access to carbohydrates from food which can break down into glucose during this time. So, the body uses other molecules for the occurrence of gluconeogenesis including amino acid, pyruvate, lactate, and glycerol instead of carbohydrates. When it produces glucose in the liver, then glucose released in the bloodstream, where it travels to cells of the whole parts of the body, so it uses energy. The gluconeogenesis process also sometimes refers to endogenous glucose production (EGP), because it needs the input of energy. Gluconeogenesis is the opposition of glycolysis, which releases a lot of energy, while It needs the input of a lot of energy. So, the process of gluconeogenesis occurs when the body has low energy. Some steps of It cannot perform in a way instead of the development of cells in different ways to perform the process.
It is another phenomenon that is used when the glucose level is low in the blood. During the process of gluconeogenesis, the molecule glycogen storage is broken down into glucose and then enters the blood. Glycogenolysis works for the formation of glucose molecule by glycogen (glucose source), while gluconeogenesis creates glucose from non-glucose source with molecules which are not made by glucose. Glycogenolysis used during a short time of fasting, as blood sugar of a person drops between meals or after a sleep of the night. While gluconeogenesis works during long period of fasting as during the time of feminine or starvation.
Difference between Glycogenesis and Glycogenosis:
Glycogenesis: Glycogenesis is the opposition of glycogenolysis; as when it produces from glucose.
Glycogenosis was also is known as glycogen storage disease (GSD), is a genetic disorder that defects the process of glycogen formation (glycogenesis) or breaks down glycogen. There are eleven distinct kinds of GSD. And 1 in 20,000-25,000 people is born with this disease in the United State. Some types of GSD are wilder than others. GSD Type II is more severe and can because of death within two years from birth. While other types of GSD refer to growth retardation of exercise.