Introduction of Vacuoles
Vacuole Definition Biology : Vacuoles are basically the storage bubbles which are found within cells. They’re found in every animal and as well as plant cells while in plants they are larger in size. Vacuoles may store food or any sort of nutrients for a cell which might be necessary for the survival of the cell. They’ll even store waste product, therefore, the remainder of the cell is protected from contamination. Eventually, those waste products would be sent out of the cell.
The structure of vacuoles is impartially informal. There’s a membrane that surrounds a mass of fluid. In this fluid very nutrients or waste product are present. Plants may additionally use vacuoles to store water. This little water baggage’s simply supporting the plant. They’re closely associated with objects known as vesicles that are found throughout the cell.
In-plant cells, the vacuoles are larger than in animal cells. Once a plant cell has stopped growing, there’s typically one dreadfully massive cavity. Typically, that cavity will take up over 1/2 the cell’s volume. This cavity can able to holds massive amount of water or food. Don’t forget that vacuoles also can hold the plant waste product. Those waste products are slowly broken into tiny items that can’t hurt the cell.
Although Vacuoles are present in both animal and plant cells, they are particularly large and abundant in plant cells, often occupying a major portion of the cell volume and forcing the remaining intracellular structures into a thin peripheral layer.
Vacuoles Structure:
These are bound by a single membrane and are formed by the coalescence of smaller vacuole during the plant’s growth and development. The membrane of the vacuole is composed of phospholipids. In the membrane-embedded proteins are present which allow the transportation of molecules.
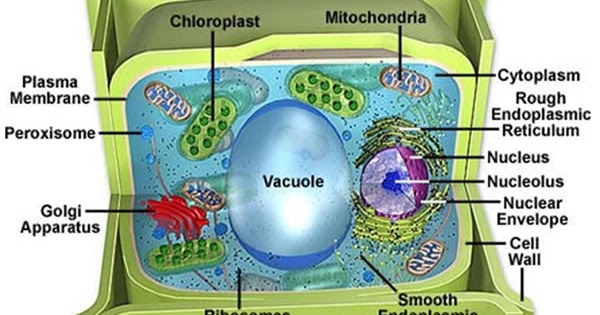
Types of Vacuoles
There are basically three types of Vacuoles:
- Central Vacuole
- Contractile Vacuole
- Food Vacuole
Central Vacuole is the specialized structures which help to maintain plants’ shape and structure by the means of water storage. They are basically hypotonic in nature.
The contractile vacuole is the type of vacuoles which helps to pumps water out of cells of Protists and also aid to stabilize the concentration.
Food vacuole is those vacuoles which help in the storage for molecules. It is basically a food source for the cell by the process of phagocytosis.
Vacuole Analogy
The best analogies for a vacuole is the Water Storage Tower, closet or storage room, refrigerator, snack cart of an airplane, and water fountains.

Vacuoles Functions:
- Vacuole of plant cells is larger than those found in animal cells. The central vacuole present in plant cells is one of the important cell organelles.
- The central vacuole, surrounded by tonoplast, offers support to cells which constitute leaves and other soft parts of plants.
- The solutes present in vacuole is known to absorb water.
- When water enters the vacuole, cells become inflated; it allows the soft parts of plants (for example, leaves) to retain their shape and turgidity.
- In short, vacuole help in maintaining the cell in proper shape.
- In animal’s cells, vacuoles play a subordinate role in the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis.
- In exocytosis, proteins and lipids are expelled from cells which is the major function of the vacuole.
- They don’t play a direct role in the extrusion of lipids and proteins.
- However, they act as containers of lipids and proteins.
- They also perform exocytosis. It is the reverse of exocytosis.
You May Also Like: Introduction of Endoplasmic Reticulum | Structure | Functions | Types
Related Articles:

