Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue Definition:
What is Epithelial tissue: It is the thin tissue that covers all exposed sides of the body. They form the digestive tract, the external skin, secretory glands, the inner lining of the mouth, the lining of hollow parts of every organ-like as lungs, heart, eyes, ear, urogenital tract, and also a ventricular system of the brain and central canals of the spinal cord.
The cells which make epithelial are usually closely bound together by special structure, known as Tight Junction. They are free from nerves and blood vessels; and they are supported by connective tissue, known as Basement Membrane.
Epithelial Tissue Function:
The function of Epithelial Tissue are described below :
The epithelial tissues perform many functions including protection from abrasion, radiation damage, chemical stress and invasion by pathogens. A single organ consists of different types of epithelial tissue.
The protective tissues are thicker, and made up of many layers of cells and also have inclusion like as keratin to give mechanical strength and for resistance. Mostly, the skin of all mammals consists layer of thick keratinized dead epithelial cell. The esophagus exposed a wide range of different textures, pH levels, and chemical compositions, it also has a protective epithelium.
In contrast, the epithelial tissues can also work for absorption, secretion, and movement of substances. These tissues are thin in appearance and often consist of cilia or microvilli and composed of one layer of cells.
Types of Epithelial Tissue:
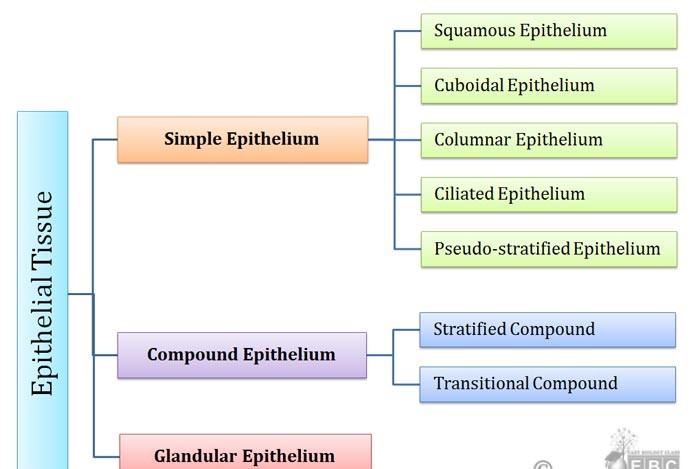
By depending on functions is a specific location, there are different types of epithelial tissues. On the base of the cell layer, the simple types of epithelial tissue are:
- Simple Epithelial
- Stratified Epithelial
The epithelium which is made up of a single layer of cell is known as simple epithelial tissue. The epithelium composed of two or more layers of the cell is known as stratified epithelial.
Epithelial tissue has three types on the bases of shape.
- Squamous epithelial tissue: These tissues consist of extremely thin cells that resemble scales of the fish.
- Cuboidal epithelial tissue: These tissues consist of cells which appear square in cross-section but longer than they are wide.
- Columnar epithelial tissue: These tissues are consists of elongated cells which involve in the absorption of materials.
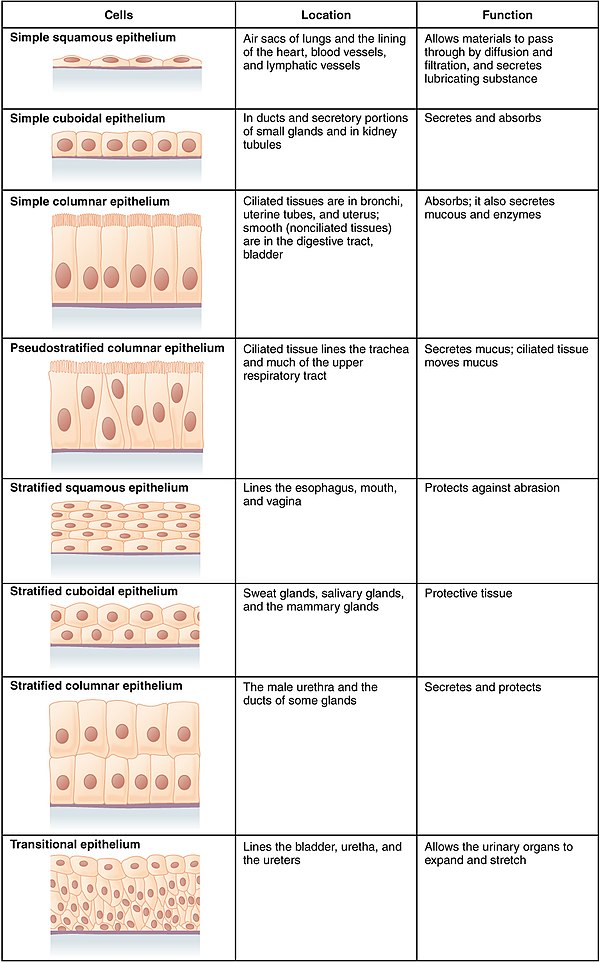
The number of cell layers and cell types together has six kinds of epithelial tissue.
- Simple squamous epithelia
- Simple cuboidal epithelia
- Simple columnar epithelia
- Stratified squamous epithelia
- Stratified cuboidal epithelia
- Stratified columnar epithelia
Examples of Epithelia:
-
Simple Epithelia:
The simple epithelia are composed of a single layer of cells that are directly in contact with the basement membrane with common apical surface. These cells may be cuboidal, squamous, or columnar.
Simple squamous epithelium lies in the alveoli of the lungs and important for gases exchanging between lungs and blood. Simple cuboidal epithelium lines the lumen of collecting ducts in the kidney and found in thyroid around follicles that extract thyroid hormones. Simple columnar epithelia lie in the female reproductive system and in the digestive tract. These cells are ciliated in fallopian tubes and involving the movement of ovum toward the uterus. In the digestive tract, they are not ciliated and consist of microvilli that give the appearance of brush bordered.
-
Stratified Epithelium:
The stratified epithelium contains more than one layer of cells and just one layer of cell in direct contact with the basement membrane. One layer of cells has an apical surface exposed to the lumen of organs or to the external environment. These tissues protect and extend friction or abrasion in the number of layers of cells. These tissues lie in the skin, with many dead keratinized cells that give protection.
Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue:
Epithelial tissues separate two structures from each other. This is achieved by the tight junction lies between two epithelial cells. The tight junction in cells also called Occluding Junctions because they prevent the flow of material. These are formed from the close interaction between extracellular domains of two sets.
Epithelial tissue has a structure known as the basement membrane. It contains two parts; the basal lamina and the reticular connective tissue underneath. The basal lamina secreted by epithelial tissue cells itself and consists of proteins, glycoproteins, and collagen. The basement membrane is important for transport nutrients, clearance of waste materials and transmission of neural signals. It also has an important role in the anchoring of epithelium to connective tissue underneath.
What type of Epithelial tissue forms the walls of the Alveoli?
Simple squamous epithelium lies in the alveoli of the lungs and important for gases exchanging between lungs and blood.
Where is Epithelial tissue found?
Simple squamous epithelium lies in the alveoli of the lungs and important for gases exchanging between lungs and blood. Simple cuboidal epithelium lines the lumen of collecting ducts in the kidney and found in thyroid around follicles that extract thyroid hormones. Simple columnar epithelia lie in the female reproductive system and in the digestive tract. These cells are ciliated in fallopian tubes and involving the movement of ovum toward the uterus. In the digestive tract, they are not ciliated and consist of microvilli that give the appearance of brush bordered.
The stratified epithelium contains more than one layer of cells and just one layer of cell in direct contact with the basement membrane.
Related Articles :
Muscle Cell | Definition, Anatomy, Types & Functions
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium | Definition, & Types